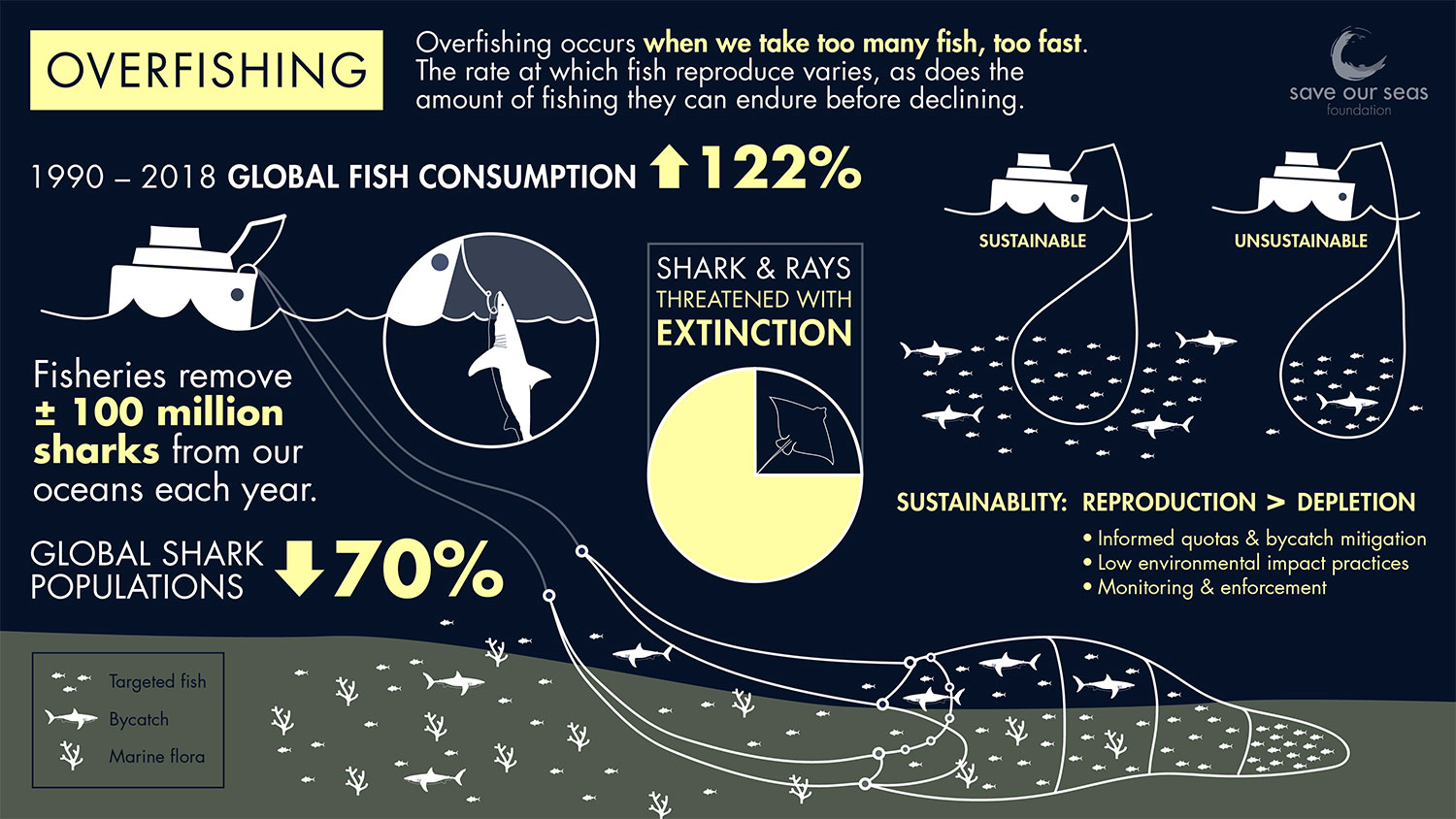
Impact of Overfishing Biology Diagrams Overfishing occurs when fish and other marine species are caught at a rate faster than they can reproduce. This unsustainable practice leads to the depletion of fish stocks, disrupting the delicate balance of marine ecosystems. Overfishing not only affects the targeted species but also has cascading effects on entire food webs.

Discover how overfishing impacts marine ecosystems, disrupting food chains, depleting fish populations, and threatening biodiversity. Learn about solutions for sustainable fishing practices to protect our oceans. How overfishing affects biodiversity Faced with the collapse of large-fish populations, commercial fleets began traveling deeper in the ocean and farther down the food chain for viable catches.
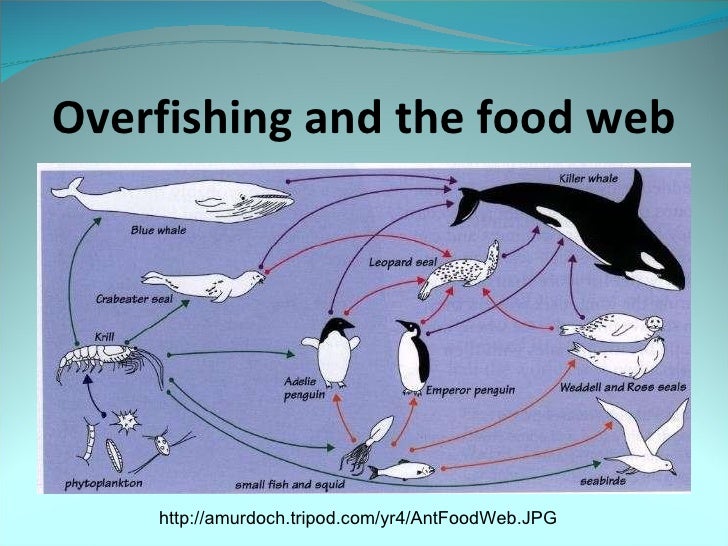
Overfishing Consequences: The Ripple Effect on Marine Ecosystems. Biology Diagrams
2. How does overfishing affect marine biodiversity? Overfishing severely impacts marine biodiversity by reducing fish populations, particularly of key species, which disrupts ecological balance and food chains. This leads to the decline or extinction of some species, the proliferation of invasive species, and the collapse of ecosystems. Overfishing significantly depletes ocean wildlife populations. Here's why it's a problem, and solutions to reduce fishing's environmental impact and maintain vital sources of food and livelihoods.

Overfishing does not only deplete fish stocks but also irreparably damages marine habitats and disrupts the delicate balance of aquatic food chains. It propels the loss of biodiversity, thereby threatening the health of the planet.

How Overfishing Impacts Marine Ecosystems Biology Diagrams
The Depletion of Fish Stocks Disruption of Food Chains The most immediate effect of overfishing is the drastic reduction in fish populations. When specific species are targeted and removed at unsustainable rates, it disrupts the intricate balance of the marine food web.